Have you ever wondered if snails have a taste for unusual delicacies? In the intriguing world of snail consumption, one question that often comes to mind is whether these slimy creatures indulge in the peculiar feast of driftwood. While it may seem peculiar, the answer is not as straightforward as one might think. Join us as we unravel the mysteries of the snail diet and explore whether these fascinating creatures have a penchant for driftwood.
What Are Snails?
Introduction to snails
Snails are fascinating creatures that belong to the mollusk family. They have a soft and slimy body, protected by a hard shell. Snails are commonly found in various habitats, including gardens, forests, and freshwater environments. They play an important role in the ecosystem by contributing to nutrient cycling and participating in the decomposition of organic matter.
Types of snails
There are numerous species of snails, each with its own unique characteristics and habitats. Some common types of snails include garden snails, pond snails, and marine snails. Garden snails are often seen in gardens and parks, while pond snails thrive in freshwater bodies such as ponds and lakes. Marine snails, on the other hand, inhabit oceans and seas.
Snail Diet
Overview of snail diet
Snails are known as herbivores, meaning they primarily feed on plant-based materials. However, their diet is not limited to just vegetation. Snails have a versatile feeding behavior that enables them to consume a variety of food sources, including plant matter, algae, decaying organic material, and even driftwood.
Vegetation and plant matter
One of the main components of a snail’s diet is vegetation and plant matter. They feed on various types of leaves, stems, flowers, and fruits. Snails are particularly fond of tender and succulent plants, such as lettuce, cabbage, and dandelions. They use a radula, a specialized feeding organ resembling a tiny file, to rasp and scrape off small portions of plant material for consumption.
Algae and biofilm
Snails also consume algae and biofilm, which are often found in freshwater and marine environments. Algae provide a valuable source of nutrition for snails, as they are rich in essential nutrients and minerals. Snails graze on rocks, logs, and other surfaces to feed on the algae and biofilm that grow there.
Decaying matter
As decomposers, snails play a crucial role in breaking down decaying organic matter. They contribute to the decomposition process by consuming dead plants, fallen leaves, and other organic debris. By consuming decaying matter, snails help to facilitate nutrient cycling and recycling in the ecosystem.
Calcium sources
Calcium is an essential mineral for snails, as it is needed for shell growth and maintenance. Snails obtain calcium from various sources, including vegetation rich in calcium, such as kale and spinach. They also consume eggshells and calcium-rich soil. However, one surprising source of calcium for some snails is driftwood.
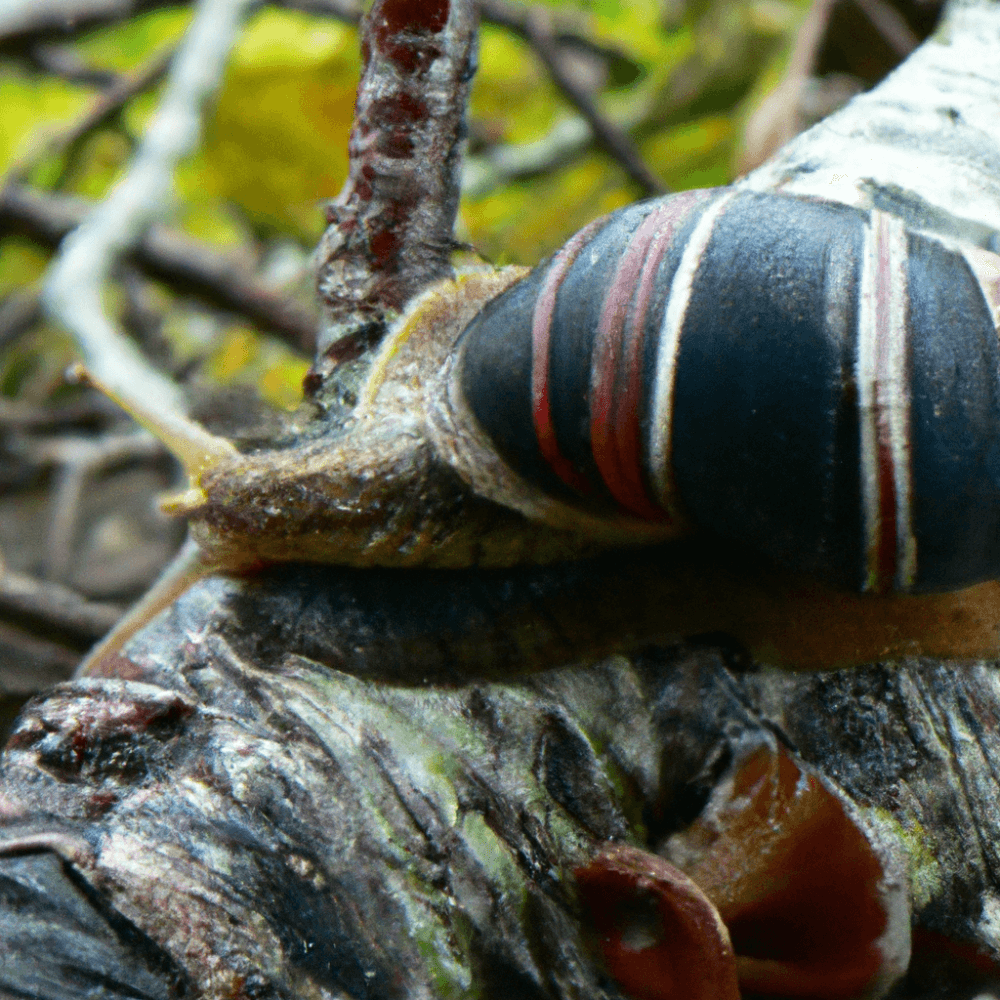

Driftwood as a Food Source
What is driftwood?
Driftwood refers to pieces of wood that have been washed ashore by rivers, tides, or waves. It is often found along coastlines and near bodies of water. Driftwood can be of various sizes and shapes, ranging from small twigs to large logs. It is formed when trees or branches fall into water bodies and are carried by currents.
Do snails eat driftwood?
Yes, certain species of snails consume driftwood as part of their diet. It may come as a surprise, as driftwood is not typically associated with food sources for snails. However, these snails have a unique ability to break down driftwood and extract nutrients from it.
Species that consume driftwood
One example of a species that feeds on driftwood is the Japanese trapdoor snail (Cipangopaludina japonica). This species is known to feed on submerged driftwood and extract nutrients from the wood fibers. Another example is the Neritina species, commonly found in marine and freshwater environments, which also consume driftwood.
Amount of driftwood consumed
The amount of driftwood consumed by snails varies depending on the species and availability of other food sources. Snails that primarily rely on driftwood as a food source may consume significant amounts to meet their nutritional requirements. However, it is important to note that not all snails consume driftwood, and for many, it is not a primary food source.
Benefits and drawbacks of driftwood as a food source
Driftwood can provide certain benefits as a food source for snails. It offers a reliable source of nutrition, including carbohydrates and minerals. Snails that consume driftwood can obtain additional nutrients, including calcium, which is vital for shell development. However, relying solely on driftwood for food can limit the diversity of nutrients available to snails. Therefore, it is essential for snails to have access to a varied diet that includes other food sources as well.
Snail Digestive System
Structure of the snail digestive system
Snails have a unique digestive system that enables them to break down and process different types of food. The digestive system starts with the mouth, where the snail ingests its food. From there, the food passes through the esophagus and enters the stomach. In the stomach, enzymes and acids help break down the food into smaller particles. The food then moves through the digestive tract, where nutrients are absorbed, and waste is formed, which is eliminated through the snail’s anus.
Ability to break down driftwood
Snails that consume driftwood have adapted digestive systems capable of breaking down the fibrous wood material. Their stomachs produce enzymes that help break down the cellulose and lignin found in wood fibers. This enables the snails to extract nutrients from the wood and utilize them for energy and growth.
Detoxifying harmful substances in driftwood
Driftwood may contain harmful substances or toxins that could be detrimental to snails. However, snails have evolved mechanisms to detoxify and eliminate these substances. Their digestive systems and excretory organs effectively process and remove any potentially harmful compounds present in the driftwood, ensuring the snail’s wellbeing.
Driftwood and Habitat
Natural occurrence of driftwood in snail habitats
Driftwood is a common feature in many snail habitats, especially those near bodies of water such as rivers, lakes, and oceans. The movement of water currents carries pieces of wood, which eventually wash up on the shores, creating a natural habitat for snails. Driftwood provides snails with a unique environment to explore, forage, and find shelter.
Importance of driftwood in maintaining habitats
Driftwood plays a crucial role in maintaining snail habitats by providing various benefits. It serves as a substrate where snails can attach themselves, allowing them to rest or hide. Driftwood also provides a surface for algae and biofilm growth, which are important food sources for snails. Additionally, the presence of driftwood creates a diverse and dynamic habitat, offering a range of microhabitats for other organisms.
Driftwood as shelter and hiding spots for snails
Snails use driftwood as shelter and hiding spots to protect themselves from predators and harsh environmental conditions. The crevices and gaps in the driftwood offer a safe refuge where snails can retreat when threatened. It also provides a moist and humid microenvironment, which is essential for snail survival and physiological functions.
The Role of Snails in Driftwood Decomposition
How snails contribute to driftwood decomposition
Snails play an important role in the decomposition of driftwood. As they feed on the wood fibers, they break them down into smaller pieces, accelerating the decomposition process. The digestive enzymes produced by snails help break down the cellulose and lignin, making the wood more accessible to other decomposers.
Interaction with other decomposers
Snails interact with a variety of decomposers present in their habitat, such as bacteria, fungi, and other invertebrates. These decomposers work together to break down the driftwood, releasing nutrients back into the ecosystem. The interactions between snails and other decomposers contribute to the overall efficiency of driftwood decomposition.
Impact on nutrient cycling
The decomposition of driftwood by snails and other decomposers plays a crucial role in nutrient cycling within ecosystems. As the wood breaks down, nutrients such as carbon, nitrogen, and phosphorus are released into the surrounding environment. These nutrients become available for other organisms, including plants, contributing to the overall health and productivity of the ecosystem.

Other Food Sources for Snails
Plants and vegetation
In addition to driftwood, snails consume a wide variety of plants and vegetation. They feed on various leaves, flowers, and fruits, depending on their preferences and availability. Snails are particularly attracted to tender and succulent plants that provide them with essential nutrients and moisture.
Algae and biofilm
Algae and biofilm serve as vital food sources for snails in freshwater and marine environments. Snails graze on rocks, logs, and other surfaces to feed on the algae and biofilm that grow there. These food sources are rich in nutrients and provide snails with the energy they need for growth and reproduction.
Decaying organic matter
As decomposers, snails contribute to the decomposition of decaying organic matter. They consume dead vegetation, fallen leaves, and other organic debris, breaking them down into smaller particles. By consuming decaying matter, snails play a crucial role in recycling nutrients and facilitating nutrient cycling in the ecosystem.
Supplementary feeding
In captivity or controlled environments, snails may require additional or supplementary feeding. Snail owners often provide commercially available snail food, which is specifically formulated to meet the nutritional needs of snails. These supplementary foods may contain a balanced combination of plant matter, algae, and other nutrients essential for snail health and growth.
Potential Risks of Consuming Driftwood
Toxic substances in driftwood
While driftwood can be a valuable food source for certain snail species, it may also contain toxic substances. The wood could have been exposed to chemicals, pollutants, or marine toxins, which can be harmful to snails if consumed. Snails need to be cautious when consuming driftwood and ensure that it is from a safe and uncontaminated source.
Effect on snail health
Consuming driftwood as a primary food source may have both positive and negative effects on snail health. While driftwood provides additional nutrients, including calcium, it may not provide a balanced diet that meets all the snail’s nutritional requirements. Snails that rely heavily on driftwood may be more prone to nutritional deficiencies or imbalances.
Possible consequences of excessive driftwood consumption
Excessive consumption of driftwood could lead to certain consequences for snails. Snails that consume too much driftwood may experience digestive issues, such as blockages or impactions. This can cause discomfort and potentially affect their overall health and well-being. It is important to ensure that snails have access to a diverse diet to minimize the risk of excessive driftwood consumption.
Mitigating risks
To mitigate the risks associated with driftwood consumption, it is recommended to provide snails with a varied diet that includes other food sources. This ensures that they receive a balanced intake of essential nutrients and minimizes the potential effects of any harmful substances that may be present in the driftwood. Adding calcium supplements to the diet can also help ensure the snails’ shell development and integrity.

Observing Snails in the Wild
Finding snails in natural habitats
To observe snails in their natural habitats, it is essential to look in suitable environments where they are commonly found. Gardens, parks, freshwater bodies, and forested areas are good places to start. Snails can often be found on rocks, plants, and even on driftwood near water bodies. Take your time to explore these areas and look closely for snails.
Observing snail feeding and foraging behavior
When watching snails, pay attention to their feeding and foraging behavior. Snails move slowly, and their feeding process is relatively leisurely. Observe how they use their radula to rasp and scrape off small portions of plant material or algae. Watch as they explore their surroundings for food, moving from one area to another in search of suitable food sources.
Snail identification tips
Identifying snails can be a fascinating challenge. Look for the distinctive shell characteristics, such as size, shape, color, and patterns. Take note of the snail’s habitat, as different species of snails can be found in specific environments. Using field guides or consulting experts can also help in the identification process. Be patient, observe closely, and enjoy the process of discovering and learning about different snail species.
Conclusion
Overview of snail diet and driftwood consumption
Snails have a versatile diet that includes a variety of food sources. While they primarily feed on vegetation, they also consume algae, decaying organic matter, and even driftwood. Driftwood can provide additional nutrients, including calcium, for snails that have adapted to consume it. However, it is important for snails to have access to a varied diet to ensure optimal health and nutrition.
Significance of driftwood in snail habitats
Driftwood plays a significant role in snail habitats by providing shelter, hiding spots, and diverse microhabitats. It also contributes to snail foraging behavior and acts as a substrate for algae and biofilm growth. The presence of driftwood creates dynamic and thriving environments for snails, supporting their survival and overall well-being.
Considerations for snail care and conservation
Understanding the dietary preferences and habits of snails is essential for their care and conservation. Providing a balanced diet and ensuring the availability of suitable food sources is crucial for snail health in captive settings. Additionally, conserving natural habitats with an abundance of driftwood is important for supporting snails and the overall biodiversity of ecosystems. By appreciating and respecting these unique creatures, we can contribute to their conservation and the preservation of their habitats.