Have you ever wondered if driftwood can burn blue? It’s a question that piques curiosity and sparks the imagination. In this article, we explore the intriguing phenomenon of driftwood burning blue and delve into the scientific explanations behind it. Get ready to embark on an illuminating journey where we uncover the secrets behind the mesmerizing blue flames that dance upon the timber.
Chemical reactions in fires
Combustion process
When a fire ignites, it undergoes a chemical reaction known as combustion. Combustion is a process where a fuel reacts with oxygen in the air, resulting in the release of heat, light, and various gases. This chemical reaction occurs at high temperatures and is integral to the sustaining of a fire.
Types of fires
Fires can be classified into different types based on their fuel source and the substances involved. Common types of fires include Class A fires (involving ordinary combustible materials like wood and paper), Class B fires (involving flammable liquids such as gasoline), Class C fires (involving energized electrical equipment), and Class D fires (involving combustible metals).
Chemical compounds in fires
Fires involve the combustion of various chemical compounds present in the fuel source. These compounds can include hydrocarbons, such as those found in wood, which release carbon dioxide and water vapor when burned. In addition to these compounds, fires may also produce toxic gases, such as carbon monoxide and nitrogen dioxide, depending on the materials involved in the combustion process.
Characteristics of driftwood
Definition of driftwood
Driftwood refers to pieces of wood that have been washed ashore by the tide or other water currents. It is commonly found along beaches or riverbanks and is characterized by its weathered appearance and smooth texture.
Composition of driftwood
Driftwood is mainly composed of various types of wood, including both hardwood and softwood species. The specific composition of driftwood can vary depending on factors such as the type of tree it originated from and the location where it was found. Some common types of wood found in driftwood include pine, oak, cedar, and birch.
Physical properties of driftwood
Driftwood exhibits several physical properties that make it unique. Due to its exposure to water and other environmental factors, driftwood is often waterlogged and has a lower density compared to regular wood. Additionally, it tends to have a more worn and smooth surface, caused by erosion and abrasion from sand and water. The shape and size of driftwood can also vary greatly, ranging from small, slender pieces to large, twisted branches.
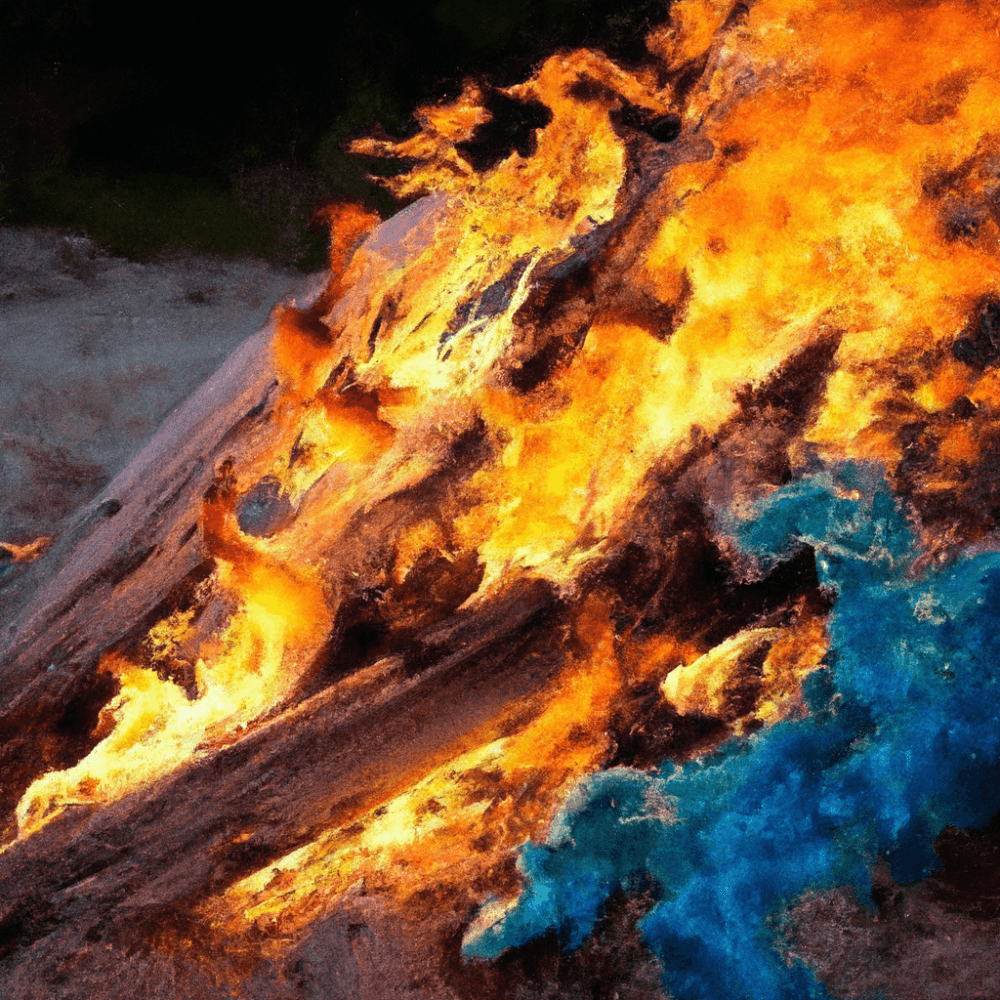
Different colored flames
Flame color and temperature
The color of a flame can be an indicator of its temperature. Generally, hotter flames tend to be bluish in color, while cooler flames appear more yellow or orange. The temperature of a flame is influenced by factors such as the type of fuel, the amount of oxygen present, and the chemical reactions occurring during combustion.
Flame color and chemical elements
Different chemical elements can contribute to the color of a flame when they are present in the fuel source. For example, the presence of copper ions can produce a green flame, while potassium compounds can result in a purple flame. The specific color produced is due to the emission of light at certain wavelengths when these elements are heated.
Common flame colors
Flames can display a wide range of colors, depending on the chemicals present. Common flame colors include yellow (from the combustion of carbon), orange (from the presence of sodium), red (from strontium or lithium), and blue (from elements such as copper or lead). These colors can add a visually striking element to fires and are often utilized in certain applications, such as fireworks displays.
Factors influencing flame color
Fuel composition
The composition of the fuel being burned is a significant factor in determining the flame color. Different species of wood, for example, have varying levels of chemical compounds present, which can result in different flame colors. This is why driftwood, with its unique composition, may display distinct flame colors compared to other types of firewood.
Presence of metallic elements
Certain metallic elements, when present in the fuel source, can influence the color of the flame. For instance, the combustion of wood containing copper impurities may produce a blue flame due to the emission of light from the excited copper atoms. Similarly, other metals like zinc, lead, and sodium can also contribute to the color spectrum of flames.
Presence of chemicals
Apart from metallic elements, other chemicals can also impact flame color. Compounds containing elements such as potassium, calcium, or strontium can generate vibrant colors when burned. These chemicals may be naturally present in the fuel source or added intentionally, as seen in various pyrotechnic displays and colored flame experiments.
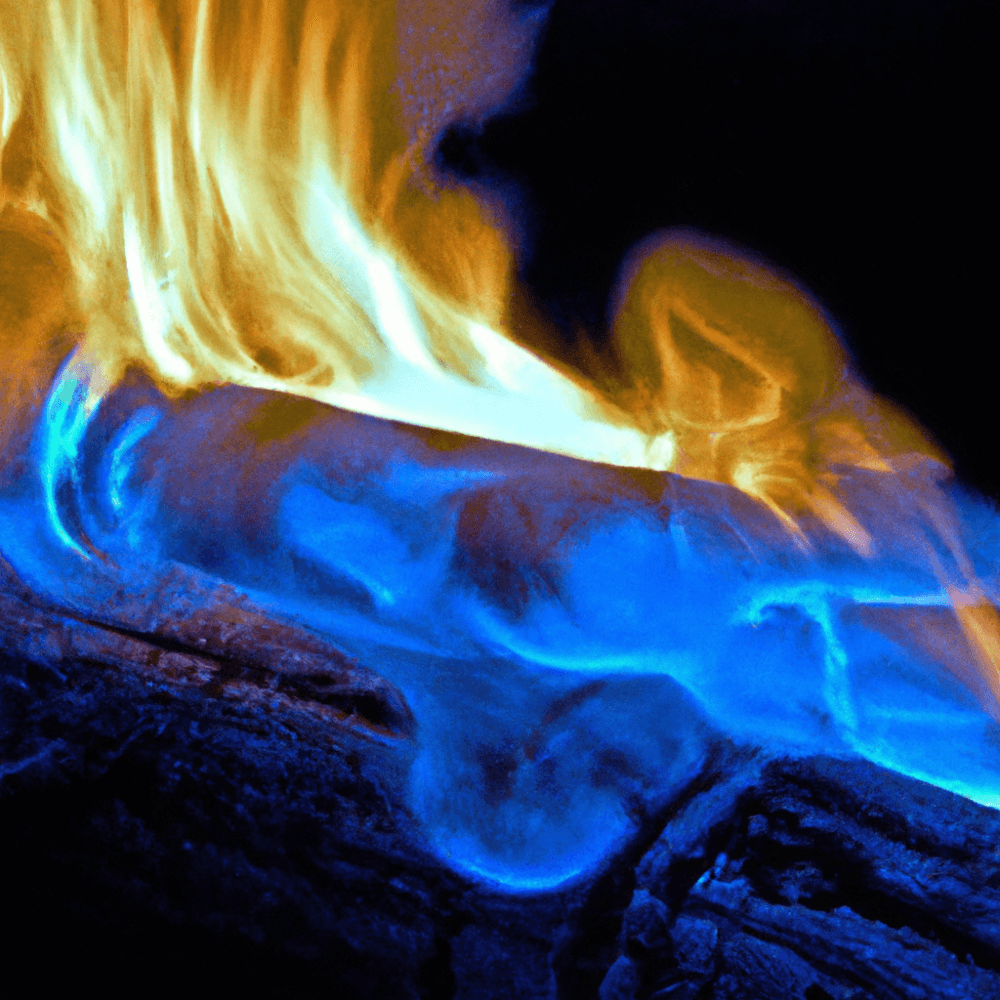

Blue flame in fires
Definition of blue flame
A blue flame is a type of flame characterized by its bluish coloration. It typically indicates a high-temperature flame and often appears more visible in low-light conditions. Blue flames are often associated with the combustion of certain gases, such as natural gas or propane.
Causes of blue flame
The blue color of a flame is primarily caused by the presence of specific chemical elements. These elements, such as copper or lead, can emit light at shorter wavelengths, which our eyes perceive as blue. Additionally, a blue flame can also result from complete combustion, where a sufficient amount of oxygen is present to burn all the fuel completely.
Chemical elements producing blue flame
Various chemical elements are known to produce blue flames when burned. Copper, for example, can give off a blue or green flame when heated. Lead, in the form of lead acetate, can also produce a blue flame. Other elements that can result in blue flames include Boron, lithium, and certain hydrocarbons found in natural gas.
Firewood and flame colors
Typical flame colors of different woods
Different species of wood can exhibit varying flame colors when burned. For instance, oak wood may produce a yellow or orange flame, while pine wood can result in a more vibrant, crackling flame with hints of orange and yellow. The unique composition of driftwood may contribute to a distinct flame color, providing a visually appealing display when used as firewood.
Explanations for different flame colors
The flame colors observed in various woods can be attributed to the presence of different chemical compounds. These compounds, such as resins and oils within the wood, can undergo combustion and release energy in the form of light. Depending on the specific compounds present and their chemical properties, different flame colors are produced.
Comparing driftwood to other firewood
Driftwood, with its exposure to water and environmental factors, possesses a distinct composition compared to regular firewood. The presence of coastal minerals and salts absorbed during its time in the ocean can contribute to the unique flame colors exhibited by driftwood. When compared to other firewood sources, such as hardwood or softwood, driftwood’s chemical makeup and exposure to coastal elements make it stand out in terms of flame color.
Burning characteristics of driftwood
Flame color of driftwood
Due to its composition and the minerals absorbed during its time in water, driftwood can produce a range of flame colors. While the exact colors observed may vary depending on the specific wood species and location, blue and green flames are often associated with the combustion of driftwood. These unique flame colors add an enchanting ambiance to fires fueled by driftwood.
Chemical elements present in driftwood
Driftwood contains various chemical elements that contribute to its flame color. These elements can include copper, manganese, iron, and sodium, among others. The presence of these elements, along with any impurities absorbed from seawater, can influence the color of the flames produced when burning driftwood.
Experiments and observations
Researchers and enthusiasts have conducted experiments to observe the burning characteristics of driftwood. These experiments have involved controlled burns of driftwood samples and careful observation of the resulting flames. The data and observations obtained from such experiments have helped shed light on the factors contributing to the distinct flame colors associated with burning driftwood.
Effects of moisture on driftwood fire
Role of moisture in combustion
Moisture plays a critical role in the combustion process of any fuel, including driftwood. When wood is damp or contains a high moisture content, it requires more energy to evaporate the water before the wood can reach its ignition temperature. This can result in a slower and less efficient combustion process.
Moisture content in driftwood
Driftwood, being in contact with water for extended periods, tends to have a higher moisture content compared to regular firewood. The waterlogged nature of driftwood can impact its burnability and the characteristics of the flames it produces. The presence of moisture can also affect the overall heat output and the time it takes for driftwood to fully burn.
Impact on flame color
The moisture content of driftwood can influence the flame color observed during combustion. Higher moisture levels can result in smokier fires and may affect the intensity or vibrancy of the flame color. Properly seasoned or dried driftwood, with lower moisture content, is likely to produce more consistent and visually appealing flame colors compared to wet or untreated driftwood.
Environmental impact of burning driftwood
Emissions from burning driftwood
Like any combustion process, burning driftwood releases various emissions into the atmosphere. These emissions can include carbon dioxide, carbon monoxide, volatile organic compounds (VOCs), and particulate matter. The amount and composition of these emissions depend on factors such as the wood species, moisture content, and combustion efficiency.
Pollution concerns
While burning wood, including driftwood, can be a sustainable and renewable energy source, it is not without environmental concerns. Incomplete combustion or the burning of treated or contaminated driftwood can release harmful pollutants into the air, contributing to air pollution and potential health risks. It is crucial to use driftwood that is free from chemicals or contaminants to minimize the environmental impact.
Sustainability considerations
The use of driftwood as a fuel source can have sustainability benefits when managed responsibly. Gathering driftwood that has naturally washed ashore reduces the demand for other non-renewable fuel sources. However, it is essential to balance this practice with environmental conservation and not disturb delicate ecosystems or protected areas.
Conclusion
Driftwood, with its unique composition and exposure to coastal elements, offers an intriguing and visually captivating option for firewood. The distinct flame colors associated with burning driftwood can add an enchanting allure to fireside experiences. However, it is important to consider the moisture content, chemical elements present, and potential environmental impact when using driftwood as fuel. By understanding the characteristics and effects of burning driftwood, we can make informed choices to enjoy its beauty while ensuring sustainability and minimizing pollution concerns. So, the next time you gather around a fire, consider the fascinating world of driftwood and the mesmerizing flames it creates.