You’re strolling along the serene shores, the gentle waves lapping at your toes as you gaze upon the mesmerizing sight of driftwood scattered along the beach. But have you ever wondered, does driftwood rot? In this captivating article, we will uncover the hidden secrets of nature’s discarded treasures, delving into the fascinating world of driftwood and its ultimate fate. So, put on your explorer’s hat, my friend, and let’s venture into the mysterious realm of driftwood decay.
Understanding Driftwood
Definition of Driftwood
Driftwood refers to pieces of wood that have been carried by water and washed ashore by waves, tides, or rivers. It is typically found along coastlines, rivers, and lakes, and can range in size from small twigs to large logs. Driftwood gets its name from the fact that it drifts or floats in the water until it reaches land.
Types of Driftwood
There are various types of driftwood, each with its own unique characteristics. Some common types include:
Beach Driftwood: This is the most common type of driftwood, found along coastal areas. It often has a weathered appearance due to its exposure to saltwater and sand.
River Driftwood: As the name suggests, this type of driftwood is found in rivers and streams. It may have a smoother texture compared to beach driftwood, as it is not subjected to the abrasive nature of sand.
Lake Driftwood: Found along the banks of lakes, this type of driftwood is usually less weathered compared to beach driftwood. It may retain more of its original color and texture.
Characteristics of Driftwood
Driftwood can display a variety of unique characteristics that make it visually appealing and sought after for decorative purposes. Some common characteristics include:
Weathering: Over time, driftwood undergoes a natural weathering process due to its exposure to the elements. This can result in a smooth, worn texture and a bleached appearance.
Texture: Driftwood often has a distinctive texture, with its surface becoming smoother through the natural erosion caused by water and sand.
Shape and Size: The shape and size of driftwood can vary greatly, depending on its origin and journey through the water. Some pieces may be small and irregular, while others can be large and sculptural.
Conditions for Rot
Moisture
One of the key factors that contributes to the rotting of driftwood is moisture. When driftwood is constantly exposed to water or high humidity environments, it creates an ideal breeding ground for microorganisms that accelerate the decay process. The presence of moisture allows fungi and bacteria to thrive and break down the wood fibers, leading to rot.
Temperature
Temperature plays a significant role in the rotting process of driftwood. Warmer temperatures promote the growth and activity of microorganisms, leading to a faster rate of decay. On the other hand, colder temperatures can slow down the rotting process. However, even in colder climates, decay can still occur over an extended period of time.
Microorganisms
Microorganisms such as fungi and bacteria are responsible for the decay of driftwood. They break down the cellulose and lignin present in the wood, releasing enzymes that facilitate the decomposition process. These microorganisms play a crucial role in the natural recycling of organic matter, including driftwood.

Process of Rotting
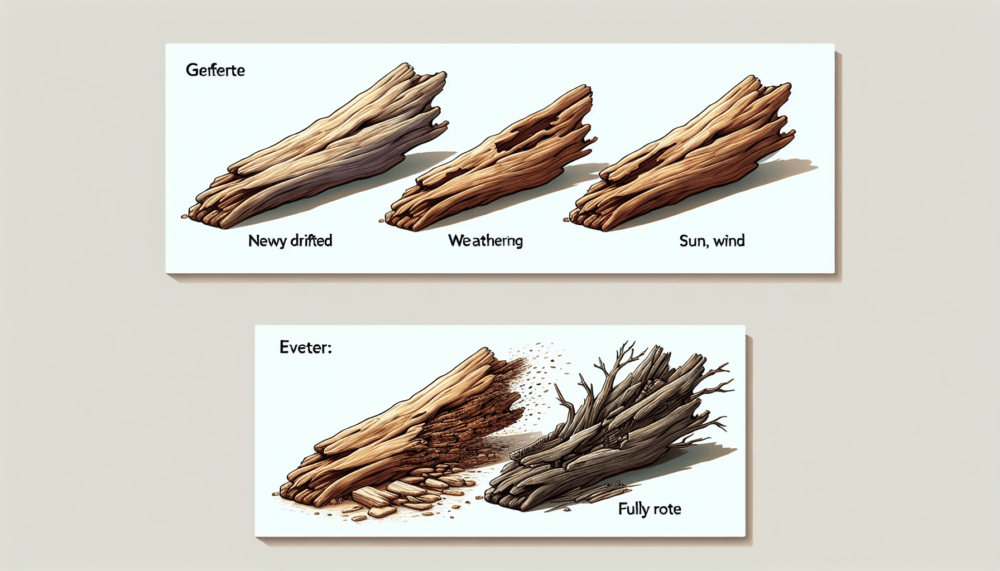
Initial Decay
The rotting process of driftwood begins with the initial decay stage. During this stage, microorganisms colonize the wood, breaking down the cellulose and lignin. Fungi, in particular, play a vital role in the initial decay process by producing enzymes that degrade the wood fibers. This stage is characterized by a softening of the wood and the appearance of discoloration or mold.
Advanced Decay
As the decay process continues, driftwood enters the advanced decay stage. At this point, the wood becomes increasingly soft and fragile, losing its structural integrity. The color of the wood may further darken, and the surface may develop a fuzzy or spongy texture. The wood fibers continue to break down, and the concentration of microorganisms increases.
Final Stages of Rot
In the final stages of rot, the driftwood becomes severely degraded and may disintegrate into smaller fragments. The wood loses its strength and may crumble or turn into a powdery substance. The microorganisms responsible for decay have consumed most of the wood fibers, leaving behind remnants that are no longer recognizable as driftwood.
Factors Affecting Rot
Driftwood Species
Different species of wood have varying levels of resistance to rot. Some types of wood, such as cedar, cypress, and teak, are naturally more resistant to decay due to their high levels of natural oils and resins. On the other hand, softer and more porous woods, such as pine or spruce, are more prone to rotting. The species of driftwood can greatly influence its susceptibility to decay.
Exposure to Elements
The exposure of driftwood to the elements also affects its rate of decay. Driftwood that remains submerged in water or constantly exposed to moisture will decay at a faster rate compared to wood that is partially or fully dried out. The length and intensity of exposure to elements like water, sunlight, and air can significantly impact the speed of rotting.
Age of Driftwood
The age of driftwood can influence its rotting process. Older driftwood that has undergone more weathering and exposure to elements may be more susceptible to rot compared to newly arrived driftwood. This is because older driftwood has had more time for microorganisms to colonize and break down the wood fibers.
Preventing Rot
Drying Driftwood
One effective method of preventing driftwood from rotting is by drying it out thoroughly. This can be achieved by placing the driftwood in a well-ventilated area and allowing it to air dry. It is important to ensure that all moisture is removed from the wood, as even small amounts can still contribute to decay. Drying the driftwood can slow down or halt the growth of microorganisms, preventing rot.
Applying Preservatives
Another way to protect driftwood from rot is by applying preservatives. These can be in the form of wood sealers or treatments that contain fungicides and insecticides. These substances can help prevent the growth of microorganisms and protect the wood from decay. It is important to follow the manufacturer’s instructions when applying preservatives and ensure they are safe for the intended use of the driftwood.
Sealing Driftwood
Sealing driftwood with a protective coating can also help prevent rot. A waterproof sealant or varnish can be applied to the surface of the wood, creating a barrier that prevents moisture from penetrating and inhibits the growth of microorganisms. The sealant should be applied evenly and allowed to cure fully before exposing the driftwood to water or other potentially damaging conditions.
Common Misconceptions
Driftwood Rotting in Water
Contrary to popular belief, driftwood does not necessarily rot when submerged in water. In fact, the continuously flowing water of rivers and streams can help reduce decay by washing away microorganisms and dispersing nutrients. However, prolonged exposure to stagnant water or being submerged for extended periods can still lead to decay.
Driftwood Rotting in Dry Environments
While driftwood may dry out in arid or dry environments, it does not necessarily mean it will not rot. Moisture can still accumulate in the wood through factors such as humidity or occasional rainfall. It is essential to ensure that any moisture present in the wood is eliminated or controlled to prevent rotting, even in dry environments.
Driftwood and Aquatic Environments
Driftwood Role in Aquatic Ecosystems
Driftwood plays a crucial role in aquatic ecosystems. It provides a habitat and shelter for various organisms, including fish, birds, and insects. The presence of driftwood in aquatic environments contributes to the overall ecosystem complexity and biodiversity. When driftwood eventually decays, it releases nutrients back into the water, enriching the ecosystem and supporting the growth of other organisms.
Rotting vs Decomposition
While driftwood eventually rots, it is important to differentiate rotting from decomposition. Rotting refers specifically to the decay of wood resulting from the activity of microorganisms. Decomposition, on the other hand, refers to the process by which organic matter breaks down and returns nutrients to the environment. Driftwood, through its eventual decay, undergoes decomposition and contributes to the natural recycling of organic material in aquatic ecosystems.
Uses of Driftwood
Decorative Purposes
Driftwood is widely used for decorative purposes due to its unique and visually appealing characteristics. It can be used to create stunning centerpieces, wall art, and even mobiles. Its weathered appearance and natural shapes provide a rustic and organic touch to any space. Driftwood can be incorporated into various styles of interior design, from coastal to bohemian.
Functional Applications
Apart from its decorative uses, driftwood also has functional applications. Its sturdy and durable composition makes it suitable for creating furniture such as benches, tables, and shelves. Additionally, driftwood can be repurposed into functional objects like candle holders, coat racks, or even serving trays. The combination of functionality and natural aesthetics makes driftwood a versatile material for practical applications.
Driftwood in Art and Design
Sculptures and Installations
Driftwood has long been used as a medium for creating sculptures and large-scale installations. Artists and designers incorporate driftwood’s natural shapes, textures, and weathered appearance to create visually captivating works of art. These sculptures and installations often celebrate the inherent beauty of the wood and its connection to nature.
Furniture and Home Decor
Driftwood is also widely utilized in the creation of furniture and home decor pieces. Its unique and organic qualities make it a popular choice for creating statement furniture pieces such as tables, chairs, and beds. Home decor items like mirrors, lamps, and picture frames can also be crafted using driftwood, adding a touch of natural elegance to any interior space.
Preserving Driftwood Art
Applying Protective Coatings
To preserve driftwood art, it is important to apply protective coatings. These coatings, such as varnishes or sealants, create a barrier that shields the wood from moisture, UV rays, and other damaging factors. Applying multiple layers of protective coatings will help enhance the longevity and durability of the driftwood art piece.
Avoiding Direct Sun Exposure
Direct exposure to sunlight can cause driftwood art to fade, dry out, or become brittle. To preserve the art piece, it is advisable to display it in an area where it is shielded from direct sunlight. If displayed near a window, the use of UV-filtering glass or curtains can help minimize the potential damage caused by prolonged sun exposure.
In conclusion, understanding driftwood involves recognizing its unique characteristics, the conditions that lead to rot, the rotting process itself, and the factors influencing rot. Preventive measures, such as drying, applying preservatives, and sealing, can be taken to prevent driftwood from rotting. It is important to debunk common misconceptions regarding driftwood rot in both wet and dry environments. Driftwood plays a vital role in aquatic ecosystems and its uses range from decorative purposes to functional applications in art and design. Preserving driftwood art involves applying protective coatings and avoiding direct sun exposure to maintain its beauty over time.