Driftwood can be an excellent source of fuel for bonfires and campfires, providing a unique and captivating ambiance. However, burning driftwood requires some careful consideration to ensure both safety and environmental consciousness. In this article, we will explore the best practices and techniques for safely burning driftwood, as well as the potential risks and alternatives to keep in mind. So, whether you’re planning a beach bonfire or simply curious about this natural fuel source, let’s discover how to burn driftwood effectively!

What is driftwood?
Definition
Driftwood refers to pieces of wood that have been washed ashore by the action of tides, waves, or rivers. This naturally occurring phenomenon typically occurs when trees or branches fall into bodies of water and are carried along by currents until they reach the coast. Driftwood can vary in size, shape, and type of wood, and is often found on beaches, river banks, or other areas near water bodies.
Characteristics
Driftwood possesses several unique characteristics that distinguish it from regular firewood. Due to exposure to water, wind, and sun, driftwood tends to be weathered, ensuring a distinct appearance with smooth surfaces and unique shapes. The wood itself may have a bleached or aged look, with a grayish coloration. Its properties can vary depending on the type of wood and the duration and intensity of exposure to the elements. This makes driftwood a visually interesting and sought-after material for various applications, including burning.
Is it safe to burn driftwood?
Hazards
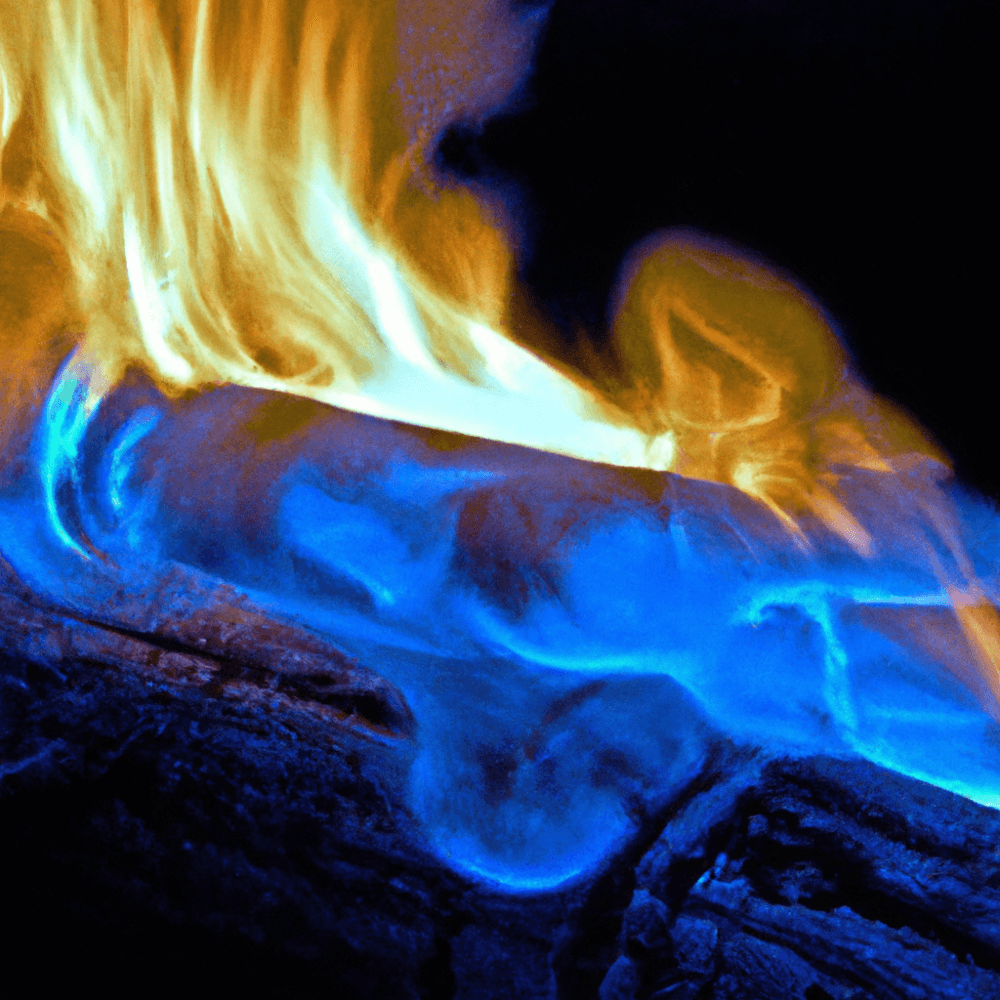
While driftwood may be an appealing choice for burning due to its aesthetic appeal, it is essential to be aware of the potential hazards associated with burning this type of wood. One of the main concerns is the presence of salt in driftwood, which can release harmful chemicals when burned. Sodium chloride and other salts found in driftwood can generate toxic fumes and release corrosive substances into the air. Inhaling these fumes can irritate the respiratory system and cause discomfort or health issues.
Environmental concerns
Apart from the health risks associated with burning driftwood, it is also important to consider the environmental impact. Driftwood serves as a valuable habitat and food source for various marine organisms, contributing to the intricate balance of coastal ecosystems. By removing and burning driftwood, you may disrupt this delicate ecosystem, adversely affecting the organisms that rely on it. Therefore, it is crucial to consider the environmental consequences before burning driftwood, as it could have far-reaching effects on the local ecosystem.
Preparing driftwood for burning
Cleaning
Before using driftwood for burning, it is important to clean it thoroughly. Over time, driftwood can accumulate dirt, sand, salt, and other debris from its time in the water. To clean driftwood, start by rinsing it with water to remove any loose dirt or sand. Next, scrub the wood with a brush and mild detergent to remove stubborn debris. Rinse the driftwood again and allow it to dry completely before using it for burning.
Drying
Another crucial step in preparing driftwood for burning is ensuring that it is adequately dried. Driftwood tends to retain moisture from its time in the water, which can hinder its ability to burn efficiently. To dry the wood, store it in a well-ventilated area for an extended period. The duration required for drying can vary depending on the thickness and moisture content of the wood. It is important to note that burning damp or wet driftwood can result in excessive smoke, difficulty in ignition, and an inefficient burn.
Choosing the right location
Outdoor burning
When burning driftwood, it is important to choose an appropriate outdoor location for safety reasons. The combustion process can produce smoke and sparks, so it is crucial to avoid burning driftwood indoors or near flammable materials. Look for an open outdoor space that is away from buildings, trees, or anything that can easily catch fire. Additionally, ensure that there are no local ordinances or regulations that prohibit open burning in your area.
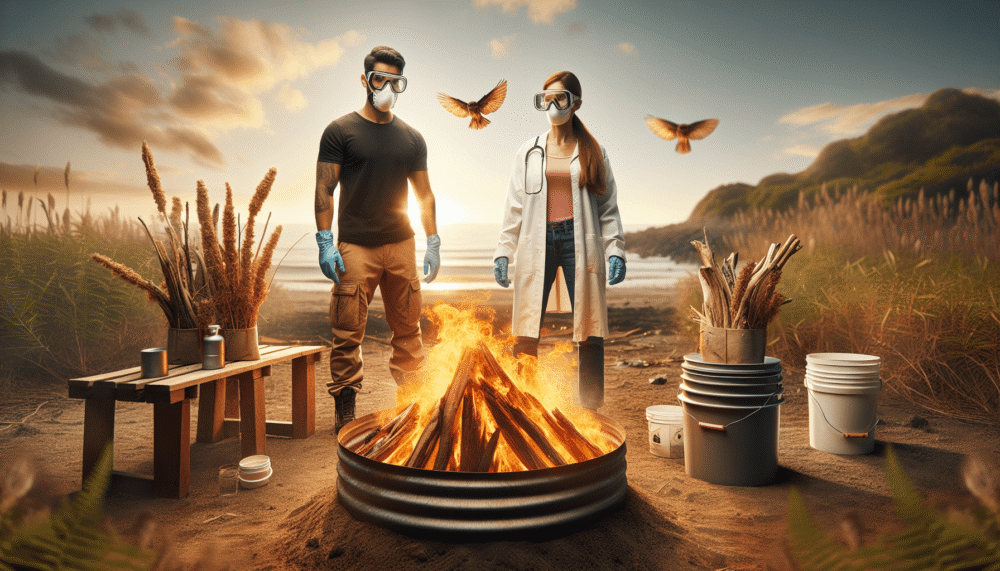
Safety precautions
Before starting a driftwood fire, take the necessary safety precautions to minimize potential risks. Clear away any dry grass, leaves, or other flammable materials around the designated burning area. Have a fire extinguisher, sand, or water nearby in case of emergencies. It is also advisable to inform neighbors about the planned burn and check weather conditions to avoid winds that could potentially spread sparks.

Building a driftwood fire
Fire pit or ring
To contain the driftwood fire and prevent it from spreading uncontrollably, it is advisable to use a fire pit or ring. These structures help create a designated area for the fire, providing additional safety and control. Fire pits or rings can be purchased or built using non-combustible materials such as stone, brick, or metal. Ensure that the size of the fire pit or ring matches the amount of driftwood you intend to burn, preventing overcrowding or potential safety hazards.
Arranging the wood
When arranging driftwood for burning, it is important to consider proper airflow and ignition. Start by creating a sturdy base layer of larger, thicker pieces of driftwood on the bottom of the fire pit or ring. This allows for proper airflow and ensures a stable foundation for the fire. Continue stacking smaller pieces of driftwood on top, leaving gaps between the wood to promote airflow and efficient burning. Avoid creating tall, unstable piles of driftwood that may collapse or spread embers.
Tips for a successful burn
Using other firewood
To enhance the burning qualities of driftwood, it can be beneficial to supplement it with other types of firewood. Mixing dry, seasoned hardwoods like oak, maple, or birch with the driftwood can help to improve the burn and provide a longer-lasting fire. These hardwoods generally have a higher energy content and burn more efficiently than driftwood alone. The combination of driftwood and other firewood varieties can result in a more enjoyable and productive burning experience.
Avoiding toxic fumes
As mentioned earlier, driftwood can release harmful chemicals when burned due to the presence of salt and other contaminants. To minimize the risk of toxic fume exposure, it is advisable to burn driftwood in well-ventilated areas with ample airflow. This helps in dispersing the fumes and reduces the concentration of any potentially harmful substances. Additionally, avoid inhaling the smoke directly and position yourself at a safe distance from the fire to minimize exposure.
Controlled burning techniques
Smaller fires
When burning driftwood, it is recommended to start with smaller fires rather than large, roaring flames. Smaller fires allow for better control and easier maintenance throughout the burn. Start by igniting a modest amount of driftwood and gradually add more as needed. This prevents excessive smoke and sparks, ensuring a controlled and manageable fire. Remember to monitor the fire closely and make adjustments accordingly to maintain a safe and efficient burn.
Monitoring the burn
Throughout the burning process, it is vital to closely monitor the fire to ensure safety and prevent any potential hazards. Keep an eye on the flames, embers, and smoke produced by the driftwood fire. Extinguish any stray embers or sparks that may pose a fire risk. If the fire becomes too intense or starts producing excessive smoke, consider adjusting the arrangement or adding additional firewood to maintain a steady and controlled burn.
Disposing of ashes
Cooling
Once the driftwood fire has burned out, it is important to properly dispose of the ashes. Before handling the ashes, allow them to cool completely. This ensures that there is no risk of burns or accidental fires. Avoid dumping hot ashes directly onto combustible surfaces or near flammable materials. Instead, transfer the cooled ashes to a non-combustible container or directly onto the soil, away from any potential fire hazards.
Proper disposal
After the ashes have cooled and been transferred, it is important to dispose of them properly. Avoid disposing of ashes in plastic bags, as they can potentially melt or ignite. Instead, consider using a designated ash container or bag made out of metal or other non-combustible materials. Some municipalities may have specific guidelines or regulations for ash disposal, so it is advisable to consult local authorities or waste management services for proper disposal methods in your area.
Alternative uses for driftwood
Decorative purposes
Apart from burning, driftwood can also be utilized for various decorative purposes. Its unique shapes, textures, and colors make it an excellent material for creating unique and eye-catching decorative pieces. Driftwood can be used in crafts, such as creating picture frames, mirrors, sculptures, or even as standalone art pieces. With a little creativity and the right tools, driftwood can add a touch of natural beauty and rustic charm to any living space or outdoor setting.
DIY projects
In addition to decorations, driftwood can serve as a versatile material for DIY projects. From constructing outdoor furniture like benches or tables to building driftwood planters or shelving units, the possibilities are endless. The weathered nature of driftwood lends itself well to projects that aim for a natural, rustic aesthetic. With proper preparation, cleaning, and creativity, driftwood can be transformed into functional and visually appealing items for your home or garden.
Conclusion
Summary
Driftwood, the wood that has been washed ashore by tides and waves, possesses unique qualities that make it visually appealing and potentially suitable for burning. However, burning driftwood comes with certain risks and considerations. The presence of salt in driftwood can lead to the release of toxic fumes when burned, posing a hazard to health and the environment. Proper preparation, cleaning, and drying of driftwood are essential steps before using it for burning.
Final thoughts
While driftwood may seem like an attractive choice for burning, it is crucial to prioritize safety and environmental consciousness. Consider alternative uses for driftwood, such as decorations or DIY projects, to make the most of its natural beauty without the health and environmental risks associated with burning. Exercise caution, following safety guidelines and local regulations, to ensure a safe and enjoyable experience when burning driftwood.