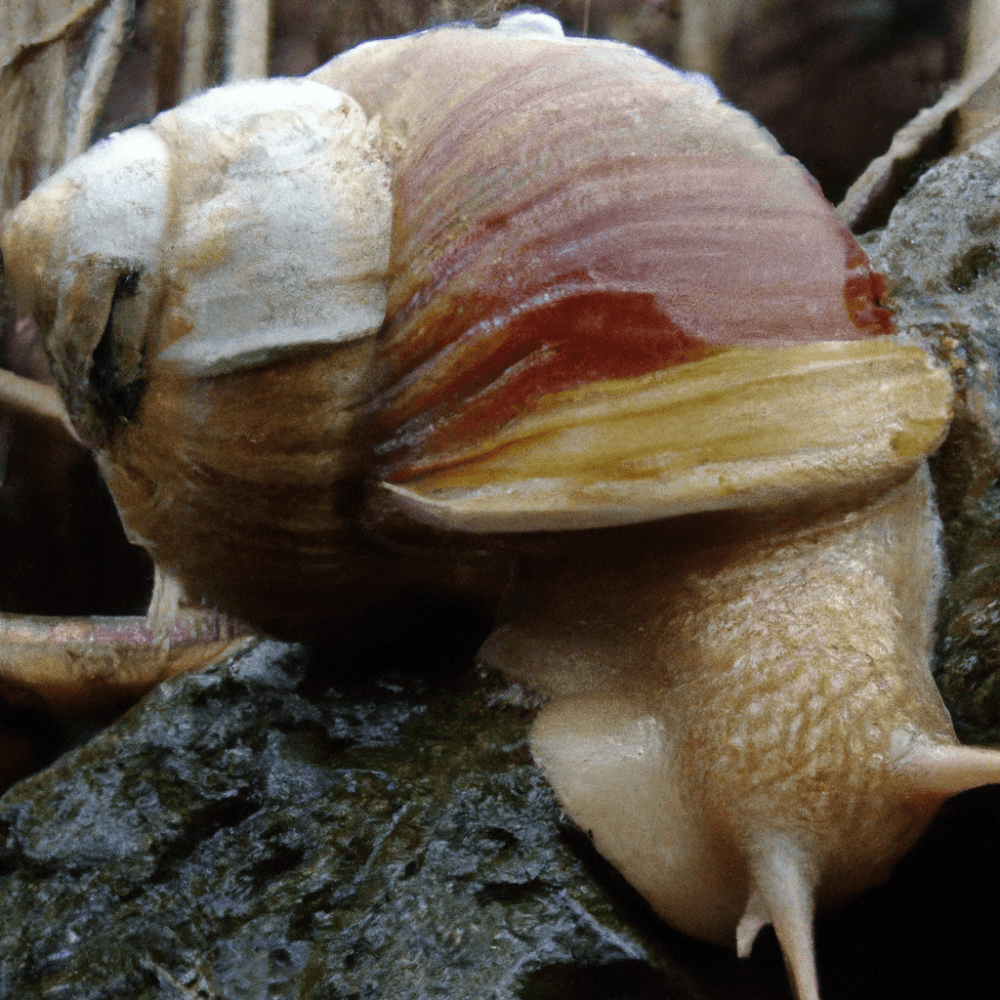
Have you ever wondered if snails have a taste for driftwood fungus? In this article, we will explore the curious relationship between snails and driftwood fungus. Snails are known to have a diverse diet, munching on various plant matter and even decaying organic material. However, the question of whether they feast on driftwood fungus remains a mystery. Let’s embark on a fascinating journey to uncover the truth behind this intriguing topic.

Do Snails Eat Driftwood Fungus?
Snails are fascinating creatures known for their slow movement and unique feeding habits. They have a wide range of diets and can be found in various habitats, including both land and aquatic environments. One interesting question that often arises is whether snails eat driftwood fungus. In this article, we will explore the relationship between snails and driftwood fungus, their feeding habits, and the potential nutritional value of driftwood fungus for these mollusks. So, let’s dive in and uncover the mysteries of snail diet!
Understanding Snail Diet
What do snails eat?
To understand whether snails consume driftwood fungus, it’s essential to have a broader understanding of their diet. Snails are omnivorous creatures, meaning they have a versatile palate. Their primary sources of sustenance include plant matter, decaying organic material, algae, and even some types of fungi. Snails play a crucial role in the ecosystem, contributing to decomposition processes and nutrient cycling.
Do snails eat wood or fungus?
While snails have been known to consume certain types of wood, their consumption of driftwood has been a subject of debate. Driftwood is essentially wood that has been washed ashore by water bodies, and it often accumulates various types of fungi, including driftwood fungus. However, whether snails actively feed on this fungus remains a topic of inquiry. Let’s explore the different types of snails and see if any of them exhibit a preference for driftwood fungus.
Types of Snails
Land snails
Land snails are the most commonly encountered snails in various terrestrial habitats. These snails have adapted to survive in diverse environments, ranging from forests to deserts. Land snails have a significant impact on ecosystems as they consume dead plant material, fungi, and algae. Some species of land snails have been observed to consume wood in their search for nutrients, but their consumption of driftwood fungus has yet to be fully established.
Aquatic snails
Aquatic snails inhabit freshwater habitats such as ponds, rivers, and lakes. They have adapted to life in the water, equipped with specialized organs for respiration and mobility. Unlike land snails, aquatic snails primarily feed on algae and other plant matter found in their watery surroundings. While some aquatic snails may consume decaying wood, it is unclear if they actively seek out or consume driftwood fungus.
Relationship Between Snails and Driftwood Fungus
Driftwood fungus as a food source for snails
Driftwood fungus refers to the various types of fungi that colonize driftwood. These fungi play a crucial role in decomposing wood, breaking it down into simpler organic compounds. The question remains whether snails actively consume driftwood fungus as a food source. While there is anecdotal evidence of snails feeding on driftwood fungus, more research is needed to confirm their preferences and determine if the fungi provide any nutritional benefits to the snails.
How snails interact with driftwood fungus
Snails are known for their ability to detect and exploit available food sources. When it comes to driftwood fungus, snails may interact with it in various ways. Some snails may graze on the fungal growth, extracting nutrients from the fungal mycelium and spores. Others may use the decaying wood as a substrate for grazing on associated algae or consuming small invertebrates attracted to the fungi. These interactions highlight the complex relationships between snails, driftwood, and the fungi that inhabit it.
Snail Feeding Habits
Mastication process
Snails have a remarkable feeding process. Their mouth is equipped with a radula, a specialized feeding organ that resembles a conveyor belt lined with tiny teeth. As a snail grazes on food, it rasps the surface, grinding it into small particles that can be ingested. The mastication process allows snails to extract both hard and soft nutrients from various food sources, including driftwood fungus if they do consume it.
Feeding frequency
Snails can exhibit a wide range of feeding frequencies depending on factors such as their species, habitat, and availability of food. Some snails feed continuously throughout the day, while others may have specific feeding periods or forage opportunistically. The feeding frequency of snails might play a role in their interaction with driftwood fungus, as they may consume it as part of their regular diet or as a supplemental nutrient source.
Feeding preferences
Snail feeding preferences can vary greatly between species. While some snails are generalists and will consume a wide range of food sources, others have more specific dietary requirements. Whether a snail includes driftwood fungus in its preferred diet may be influenced by factors such as its natural habitat, availability of other food sources, and even genetic predispositions. Further research is needed to understand the specific feeding preferences of different snail species regarding driftwood fungus.
Driftwood Fungus
What is driftwood fungus?
Driftwood fungus refers to the fungi that colonize driftwood, typically wood that has been washed ashore by bodies of water. These fungi belong to diverse taxonomic groups, including Ascomycota, Basidiomycota, and Zygomycota. Driftwood fungus plays a vital ecological role in the decomposition process, breaking down the wood’s complex organic compounds into simpler forms. While driftwood fungus can harbor a variety of organisms, including snails, the extent of snail-fungus interactions is still being explored.
Characteristics of driftwood fungus
Driftwood fungus exhibits unique characteristics that allow it to thrive in harsh environments. These fungi have adaptations that enable them to withstand exposure to water and fluctuations in moisture levels. Driftwood fungi are often specialized for wood decay, possessing enzymes that break down the complex polymers present in the wood’s cell walls. Some species produce fruiting bodies that release spores, aiding in their dispersal and potential colonization by other organisms.
Nutritional Value of Driftwood Fungus
Fungal nutrients
Driftwood fungus contains a diverse array of nutrients that could potentially benefit snails. Fungi are known to produce essential amino acids, vitamins, and minerals. The decomposition of wood by driftwood fungus releases nutrients that can be absorbed and utilized by organisms such as snails. However, the specific nutritional value of driftwood fungus for snails is yet to be fully understood.
Benefits for snails
Snails are known to have relatively low metabolic rates, requiring a diet rich in nutrients for their growth, reproduction, and general well-being. If snails do consume driftwood fungus, it could provide them with a valuable source of additional nutrients. This could be particularly beneficial in habitats where other food sources are limited or during specific life stages when nutrient requirements are higher.
Snails and Decomposition Processes
Contribution to decomposition
Snails play a vital role in the decomposition process by consuming dead plant material and fungi, including driftwood fungus. By feeding on decaying organic material, snails help break down complex organic compounds into simpler forms, facilitating the recycling of nutrients back into the ecosystem. Without snails and other decomposers, the accumulation of dead plant matter and wood debris would impede nutrient cycling and hinder the health of the environment.
Role in nutrient cycling
Nutrient cycling is a critical process in any ecosystem, ensuring the availability of essential elements for the growth of plants and other organisms. As snails feed on driftwood fungus and other organic matter, they incorporate these nutrients into their bodies. When snails excrete waste, they release these nutrients back into the environment, making them accessible to other organisms. This cyclical process of nutrient uptake and release by snails contributes to the overall health and productivity of ecosystems.
Predators of Snails
Natural threats to snails
Snails face numerous challenges from natural predators that target them for food. Predators of snails vary depending on their habitat but can include birds, mammals, reptiles, and other invertebrates. Some predators have developed specialized adaptations to feed on snails, such as beaks or jaws designed to crush their shells. These predation pressures can impact snail populations, affecting their abundance and distribution in the ecosystem.
Impact on snail populations
The presence of predators can significantly influence snail populations. When predation rates are high, snails may alter their behavior, seeking refuge in protective microhabitats or becoming more active during specific times to avoid encounters with predators. Additionally, predation can contribute to shaping the evolution of snails, leading to the development of defensive mechanisms or changes in shell morphology. Understanding these predator-prey dynamics is crucial to conservation and management efforts for snail populations.
Conservation and Management
Conservation efforts
The conservation of snails and their habitats is essential for maintaining the integrity of ecosystems. Many species of snails are under threat due to habitat loss, pollution, and climate change. Efforts to conserve snails often involve protecting their habitats, creating nature reserves, and implementing measures to reduce human impacts on their populations. By conserving snails, we can preserve their ecological roles, including their contributions to decomposition processes and nutrient cycling.
Managing snail populations
In some cases, managing snail populations may be necessary to prevent ecological imbalances or address specific issues. This management can involve measures such as controlling invasive snail species that can outcompete native snails or cause harm to agricultural crops. Careful consideration should be given to the potential impacts of management strategies to ensure they are sustainable and do not inadvertently harm other organisms or disrupt natural ecosystems.
In conclusion, the question of whether snails eat driftwood fungus remains somewhat unresolved. While snails are known to consume certain types of wood and fungi, their specific interactions with driftwood fungus are still being explored. Snails have diverse diets and can be found in both land and aquatic environments, playing crucial roles in decomposition processes and nutrient cycling. Understanding the nutritional value of driftwood fungus and the relationship between snails and this fungal resource requires further research. By uncovering the intricacies of snail feeding habits and their interactions with driftwood fungus, we can gain valuable insights into the complex web of life that exists within our natural habitats.