{
“@context”: “https://schema.org”,
“@type”: “Article”,
“headline”: “Exploring the Elegance of Drift Wood Art Creations”,
“description”: “Drift wood art is a captivating form of artistic expression that melds the raw beauty of nature with human creativity. This unique art form utilizes pieces of driftwood, which are naturally weathered and shaped by the elements, to create stunning sculptures and installations.”,
“image”: [
“https://driftwood4us.com/wp-content/uploads/2025/09/g00bc57cb7ce5d982ecfd78c62dae4b26a7341cb908790d5675c3064a8dff5c5dddf468236b1fd909967737543888a3af_640.jpg”,
“https://driftwood4us.com/wp-content/uploads/2025/09/g8596ccae184b9d3b441d7f5b792b020de2569734bffeab91be35ad6cdc3ee2658786de6c64e12acc5f1cd563e853d23a_640.jpg”,
“https://driftwood4us.com/wp-content/uploads/2025/09/g9ff28c76ab7a091c50e96835eef9f66435ddeea321d8c67a656e51ebe7696abda5aac2feae12a0ca82b9b8ca4beb9043_640.jpg”
],
“datePublished”: “2025-09-14T11:58:22Z”,
“dateModified”: “2025-09-14T11:58:27Z”,
“author”: {
“@type”: “Organization”,
“name”: “Driftwood 4 Us”,
“url”: “https://driftwood4us.com”
},
“publisher”: {
“@type”: “Organization”,
“name”: “Driftwood 4 Us”,
“url”: “https://driftwood4us.com”,
“logo”: {
“@type”: “ImageObject”,
“url”: “https://driftwood4us.com/wp-content/uploads/logo.png”
}
},
“mainEntityOfPage”: {
“@type”: “WebPage”,
“@id”: “https://driftwood4us.com/exploring-the-elegance-of-drift-wood-art-creations/”
},
“articleSection”: “Art & Crafts”,
“keywords”: [
“driftwood art”,
“drift wood creations”,
“natural art”,
“sustainable art”,
“wood sculptures”,
“eco-friendly art”,
“beach art”,
“natural materials”,
“artistic expression”,
“recycled art”
],
“about”: [
{
“@type”: “Thing”,
“name”: “Driftwood Art”,
“description”: “An artistic practice that uses naturally weathered wood pieces to create sculptures and installations”
},
{
“@type”: “Thing”,
“name”: “Sustainable Art”,
“description”: “Art forms that emphasize environmental responsibility and use of recycled materials”
},
{
“@type”: “Thing”,
“name”: “Natural Sculptures”,
“description”: “Three-dimensional artworks created from materials found in nature”
}
],
“mentions”: [
{
“@type”: “Thing”,
“name”: “Wood Carving”,
“description”: “The art of shaping wood using cutting tools”
},
{
“@type”: “Thing”,
“name”: “Environmental Art”,
“description”: “Art that addresses environmental issues or uses natural materials”
},
{
“@type”: “Thing”,
“name”: “Beach Combing”,
“description”: “The activity of searching beaches for interesting objects washed ashore”
}
],
“wordCount”: 487,
“inLanguage”: “en-US”,
“isAccessibleForFree”: true,
“genre”: “Educational Article”,
“articleBody”: “Drift wood art is a captivating form of artistic expression that melds the raw beauty of nature with human creativity. This unique art form utilizes pieces of driftwood, which are naturally weathered and shaped by the elements, to create stunning sculptures and installations. The elegance of drift wood art lies in its ability to transform the ordinary into the extraordinary, offering an organic aesthetic that is both timeless and modern.”
}
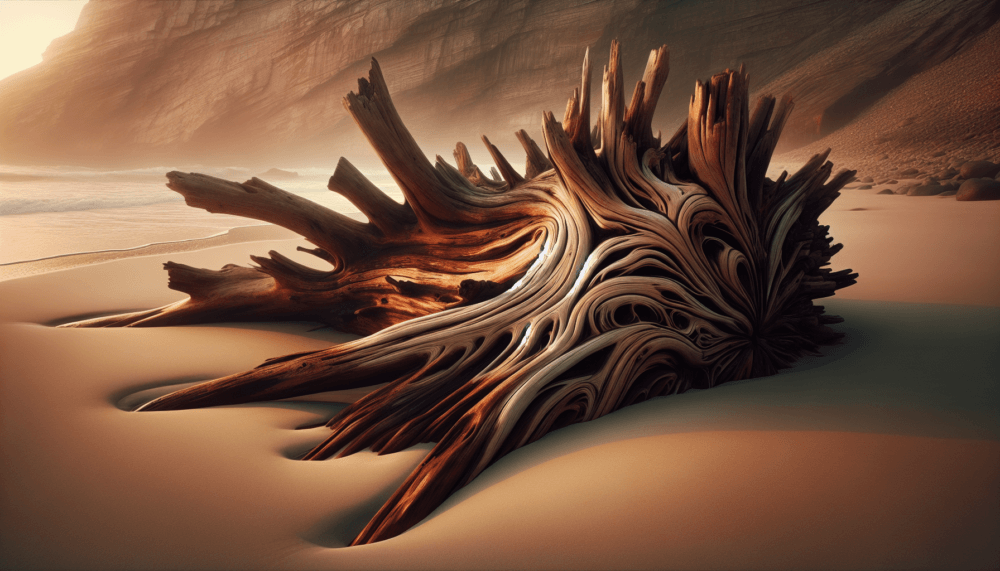
Drift wood art is a captivating form of artistic expression that melds the raw beauty of nature with human creativity. This unique art form utilizes pieces of driftwood, which are naturally weathered and shaped by the elements, to create stunning sculptures and installations. The elegance of drift wood art lies in its ability to transform the ordinary into the extraordinary, offering an organic aesthetic that is both timeless and modern.
Understanding Drift Wood Art
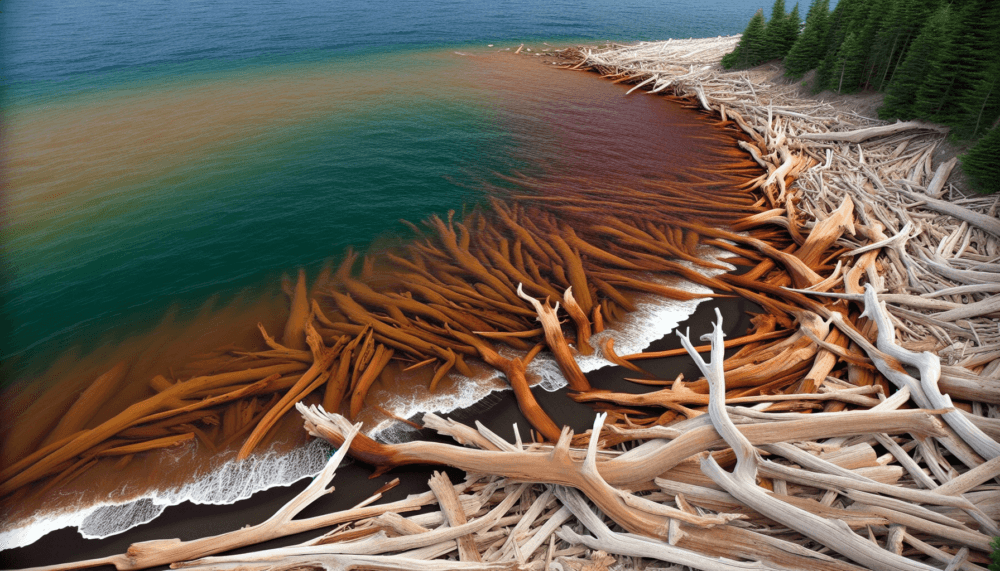
Drift wood art involves the use of wood that has been washed ashore by rivers, lakes, or oceans. This wood is often sculpted by the natural forces of water, wind, and sand, resulting in distinct shapes and textures that artists can work with. The art form is not only a testament to nature’s artistry but also a celebration of sustainability, as it repurposes materials that would otherwise be overlooked.
The Artistic Process
The process of creating drift wood art begins with the collection of suitable pieces. Artists often look for wood with unique shapes, interesting grain patterns, and varied sizes. Once collected, these pieces are cleaned and sometimes treated to preserve their natural beauty. The artist then employs various techniques such as carving, assembling, and finishing to bring their vision to life.
Carving and Assembly
Carving is a crucial step in transforming driftwood into art. Artists may use tools ranging from simple knives to advanced power tools to shape the wood into desired forms. In addition to carving, the assembly of multiple pieces can create more complex and intricate artworks. This aspect of drift wood art allows for limitless creativity, as artists can combine different pieces to form sculptures that are both abstract and representational.
Finishing Touches
Finishing involves the application of oils, varnishes, or paints to enhance the wood’s natural appearance and ensure longevity. Some artists prefer to leave the wood in its natural state, allowing its inherent beauty to shine through. The choice of finish can greatly influence the final look of the artwork, adding depth and vibrancy to the piece.
Significance and Appeal
The appeal of drift wood art lies in its ability to connect us with nature while also showcasing human ingenuity. Each piece tells a story, capturing the journey of the wood from its origins to its final transformation.  . This art form is particularly valued for its eco-friendly nature, as it promotes the use of sustainable materials in artistic creation.
. This art form is particularly valued for its eco-friendly nature, as it promotes the use of sustainable materials in artistic creation.
- Sustainability: Drift wood art emphasizes recycling and reusing natural resources.
- Uniqueness: No two pieces of drift wood are alike, ensuring that each artwork is one-of-a-kind.
- Aesthetic Appeal: The natural textures and shapes of driftwood offer a rustic yet refined look.
The Future of Drift Wood Art
As environmental awareness continues to grow, drift wood art is likely to gain even greater prominence. Artists are increasingly drawn to sustainable practices, and driftwood provides a perfect medium for those seeking to create beautiful, eco-conscious art.  . This art form not only enriches the cultural landscape but also inspires a deeper appreciation for the natural world.
. This art form not only enriches the cultural landscape but also inspires a deeper appreciation for the natural world.